Global Economic Outlook Dims Amid Trade Shifts and Policy Uncertainty, IMF Reports
The global economy is navigating a period of significant transition, marked by rising trade protectionism, persistent policy uncertainty, and subdued growth prospects, according to the International Monetary Fund’s October 2025 World Economic Outlook.
Growth Slows as Resilience Fades
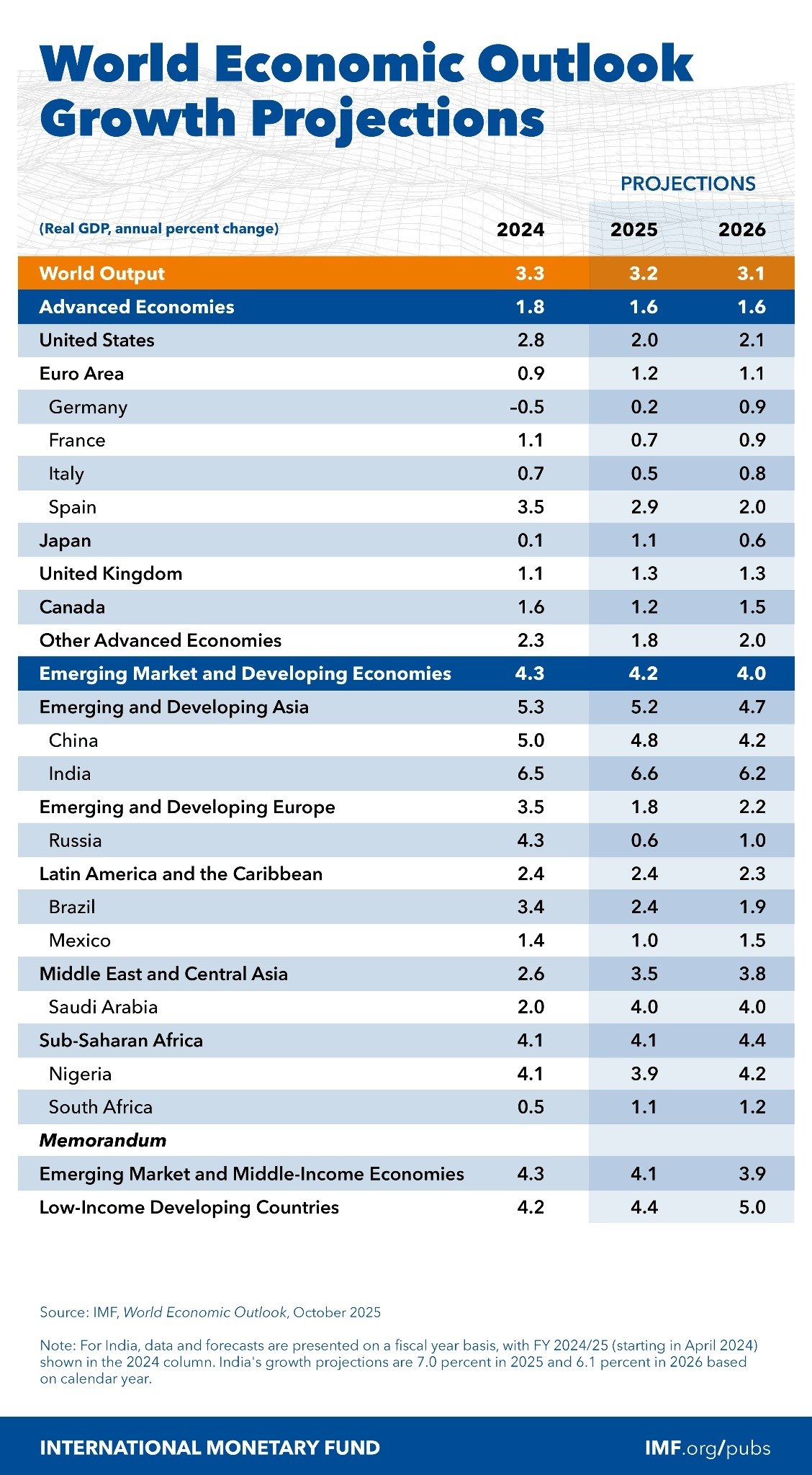
Global growth is projected to decelerate from 3.3% in 2024 to 3.2% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026. While this represents a slight improvement from mid-year forecasts, it still reflects a cumulative loss of 0.2 percentage points compared to pre-tariff projections from October 2024. The slowdown is largely attributed to the effects of new U.S. tariffs and heightened trade policy uncertainty, which have dampened investment and clouded the economic outlook.
Advanced economies are expected to grow by just 1.6% in both 2025 and 2026, with the U.S. slowing to 2.0% this year. Emerging market and developing economies will also moderate, expanding by 4.2% in 2025 and 4.0% in 2026.
Trade Tensions and Supply Chain Adjustments
A key driver of the shifting landscape has been the U.S. imposition of tariffs on a broad range of trading partners, lifting effective tariff rates to levels not seen in a century. Although subsequent negotiations have moderated some extremes, trade policy uncertainty remains elevated. Early data suggest that trade is being rerouted, with Chinese exports to the U.S. declining and diversifying toward Asian and European markets.
Despite initial resilience—supported by front-loading of imports and favorable financial conditions—the IMF warns that the full impact of tariffs and uncertainty may still be ahead. Pass-through to consumer prices, particularly in the U.S., has so far been limited but is expected to increase.
Inflation Paths Diverge
Inflation trends are increasingly varied across regions. In the U.S., inflation is projected to rise to 2.7% in 2025, up from earlier forecasts, partly due to tariff effects. In contrast, many emerging economies in Asia are experiencing lower-than-expected inflation, aided by declining food and energy prices. Globally, inflation is expected to ease to 4.2% in 2025 and 3.7% in 2026.
Risks Tilted to the Downside
The report highlights several downside risks:
· Prolonged trade uncertainty and further protectionist measures could disrupt supply chains and dampen investment.
· Tighter immigration policies in advanced economies may reduce labor supply and potential output.
· Fiscal vulnerabilities, especially in highly indebted countries, could interact with rising borrowing costs.
· A potential correction in overvalued AI-related stocks poses financial stability risks.
· Erosion of central bank independence and data integrity could undermine policy credibility.
On the upside, breakthroughs in trade negotiations, stronger-than-expected AI productivity gains, or accelerated structural reforms could improve the outlook.
Policy Priorities: Stability, Predictability, and Reform
The IMF urges policymakers to focus on restoring confidence through predictable and sustainable measures:
· Trade Policy: Countries should establish clear, rules-based trade roadmaps to reduce uncertainty and avoid fragmentation.
· Fiscal Policy: Credible medium-term consolidation is needed to rebuild buffers and ensure debt sustainability, particularly as public debt levels continue to rise.
· Monetary Policy: Central banks should maintain independence and calibrate policies to domestic conditions, avoiding premature easing where inflation persists.
· Structural Reforms: Investments in education, digitalization, and labor mobility are essential to lift medium-term growth, especially as industrial policies carry high fiscal costs and risks of misallocation.
Conclusion
While the global economy has shown resilience in the face of recent shocks, the IMF cautions that the outlook remains fragile. A coordinated approach to policy—emphasizing predictability, cooperation, and reform—will be crucial to navigating this period of flux and laying the foundation for more stable and inclusive growth.





